With Internet of Things (IoT) we refer to the process of connecting physical objects of daily use to the Internet; potentially, each object can acquire its own identity in the digital world.
The idea behind the IoT is to make objects “intelligent” by interconnecting them, in order to exchange information owned, collected and / or processed.
A borderless paradigma
The Internet of Things is a paradigm that does not know, potentially, application boundaries: from cars that communicate with the road infrastructure to prevent accidents (smart mobility), to household appliances that coordinate to optimize the use of power ( smart home), to the production plants that exchange data with the products for the management of their life cycle, etc.
Each object can be made intelligent, that is, connected and communicating. By becoming “talking”, things allow us to inaugurate a horizon of new services capable of improving the quality of our life and our work. Everything becomes smart: more intelligent, more comfortable and more useful.
The starring in the IoT network
The undisputed protagonists of IoT systems are sensors, that is all those devices that allow to collect data that are then analyzed and processed in order to produce the knowledge necessary to react and make decisions. Decisions that can also be made by the objects themselves (eg: Smart Building).
There is a wide range of devices that can be inserted into an IoT network: from video cameras, to light detectors, to motion and proximity sensors to sound sensors, and so on.
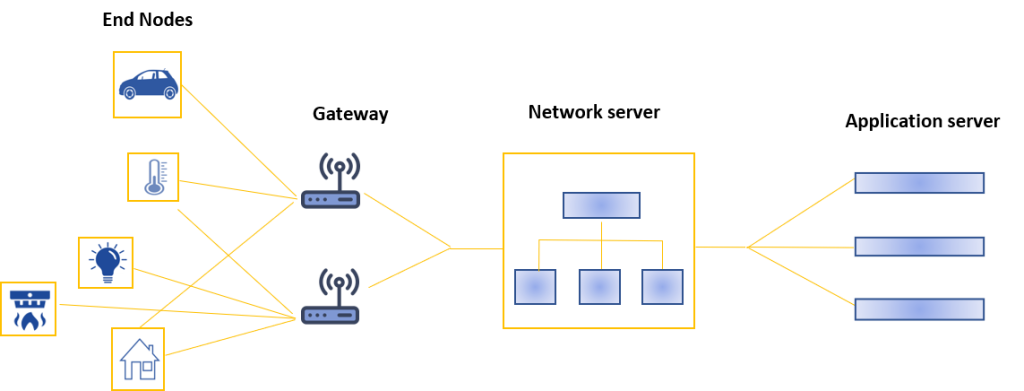
The data collected by the sensors are aggregated by the gateway which, through the network, transmits them to other devices; in order to “talk”, the sensors must be connected.
The connection at the base of the IoT network
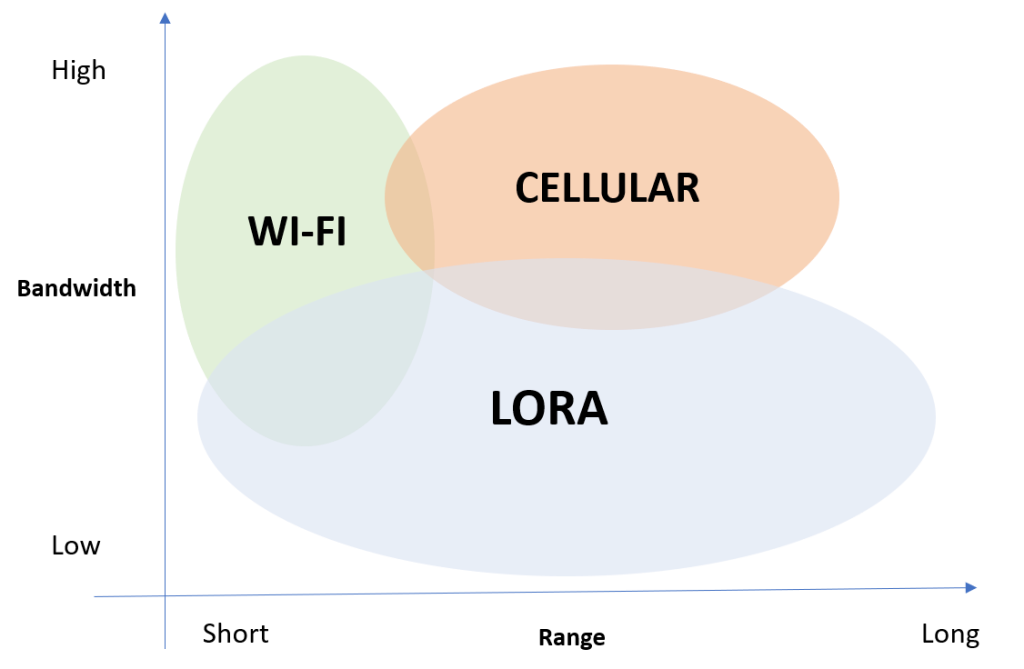
Traditional networks, which we normally rely on to obtain connectivity (Wi-Fi or 3G / 4G) bring with them various problems; to better understand, we report some wireless technologies in a graph, grouping them by range of action and bandwidth.
Cellular communications (such as 2G, 3G, 4G, indicated in the orange area) transfer medium to large amounts of data over a wide range of coverage; they are certainly suitable for outdoor use. For the purposes of the IoT network, however, the cost of the technology appears excessive.
The wireless technologies (in green) are also suitable for communications of medium to large amounts of data but within a range of a few meters, therefore ideal for indoors. They do not require a subscription and therefore have a reduced cost. However they do affect the battery life which should be changed too often.
LoRa, on the other hand, is a Low power wide area technology, which facilitates the development of networks in which nodes require “low mobility” and very limited data exchange, and are characterized by very low energy consumption.
LoRa becomes LoRaWAN when to the physical layer we add the MAC (Media Access Control) layer necessary to extend the communication to the internet.
What is LoRaWAN?
The LoRa Alliance describes LoRaWan as “a Low Power, Wide Area (LPWA) network protocol designed to wirelessly connect battery-powered ‘objects’ to the Internet in regional, national or global networks and addresses the key requirements of the Internet of Things (IoT) such as two-way communication, end-to-end security, mobility and location services. “. The LoRaWAN protocol is a Low Power Wide Area Networking (LPWAN) communication protocol that runs on LoRa. The LoRaWAN specification is open so that anyone can set up and manage a LoRa network.
Main features:
- Long range: allows a throw of up to 50 km.
- Low battery consumption: LoRa technology allows to obtain a sensor battery life of over 10 years.
- Bi-directional communication.
- Geolocation: allows localization without the need for GPS.
- Cost reduction: infrastructure, maintenance costs, the cost of sensors.
- Interoperability: any LoRaWan sensor can be connected to an existing network.
- Security: data is end-to-end encrypted.
Solutions by Softech
The IoT sensors developed by Softech communicate via the LoRaWAN protocol and are equipped with specific software for analyzing the data collected from a cognitive and / or predictive point of view.
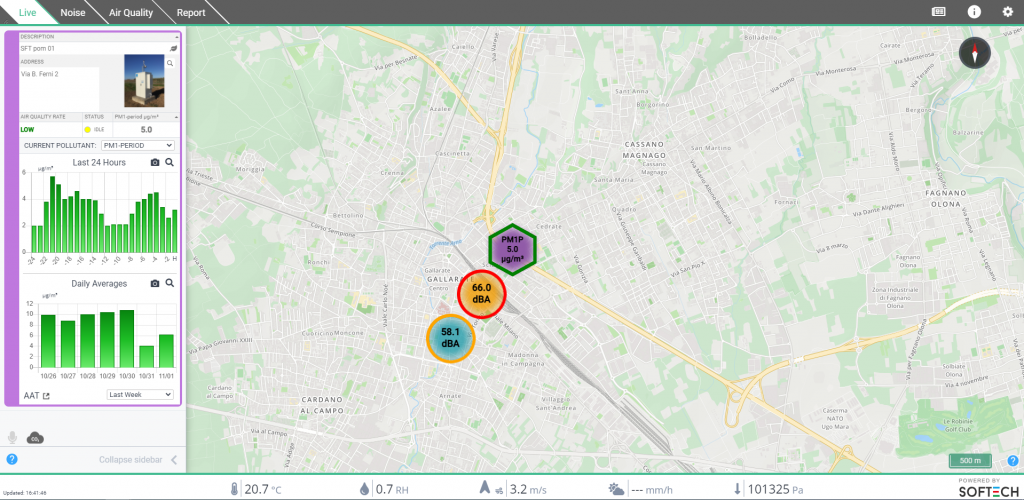
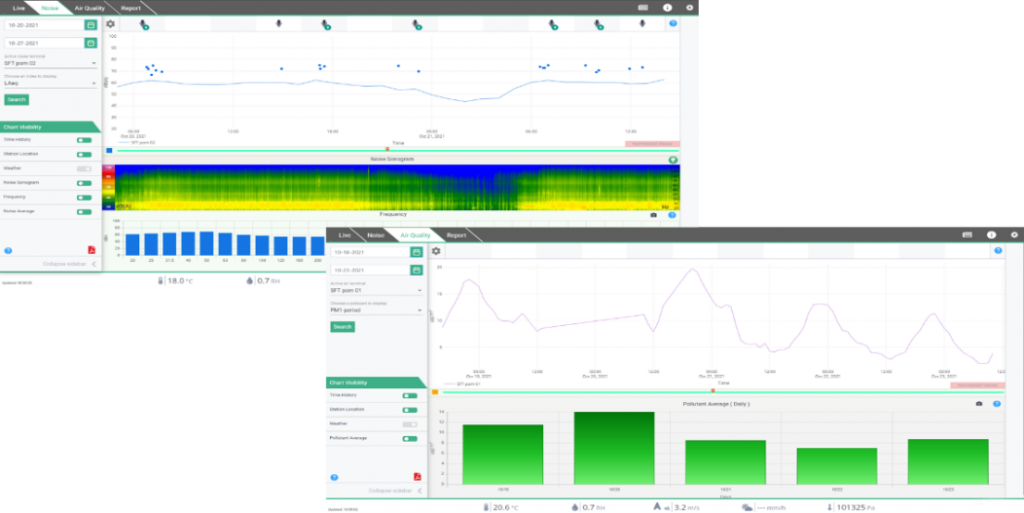
In our portfolio of IoT solutions, systems dedicated to SMART CITY, thanks to which it is possible to detect data: on traffic, on the use of a certain service, on air quality, on vibrations and noises … but also data relating to the geolocation of infrastructures (such as parking for the disabled, charging stations for electric vehicles, etc.) or on the frequency of transit of means of transport or access to a digital platform, etc.
In particular, we have devised a SMART PARKING system that is particularly innovative because it is not intended for monitoring stalls, but aimed at facilitating control by the competent authorities and making the city areas safe.
Moreover
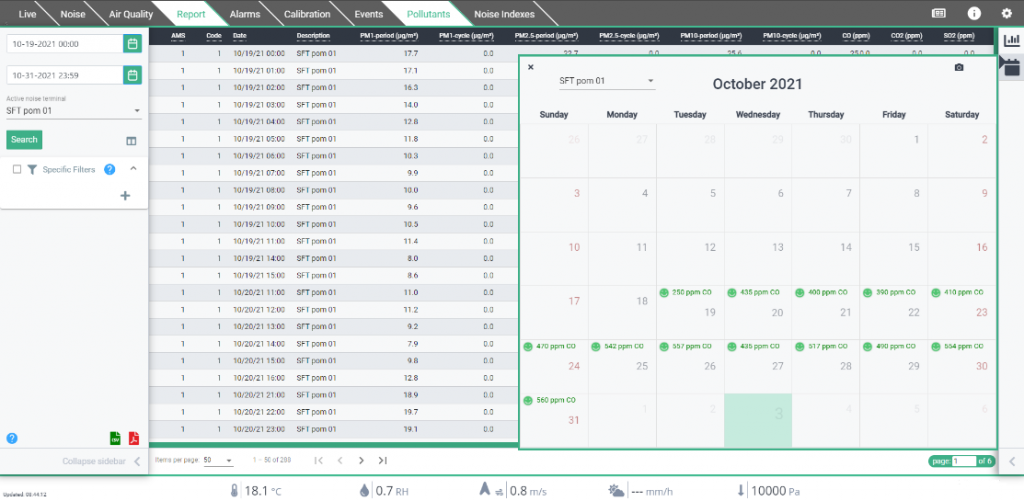
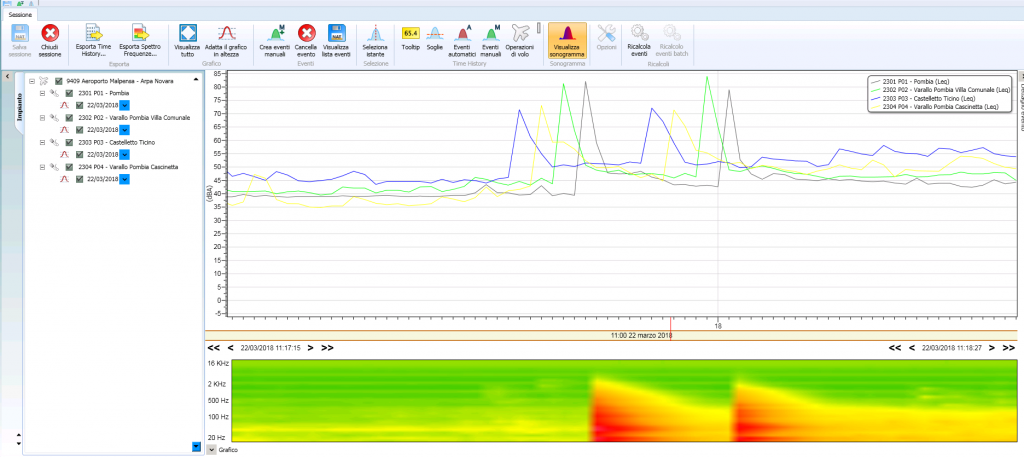
With the appropriate adjustments, the IoT can also be used for developments with a view to SMART BUILDING: and this is exactly what our SARA IoT system does, which allows you to monitor multiple factors (not only environmental ones) inside the airports, and to activate intelligent responses when certain thresholds are reached. The system can also be applied to contexts other than the airport, such as public offices and smart buildings.
Also on the motorway, with the same technology, we have created a system for SAFETY in parking areas which is characterized by reduced costs, ease of installation and the possibility of integration with sensors for other functions (click here to find out more).