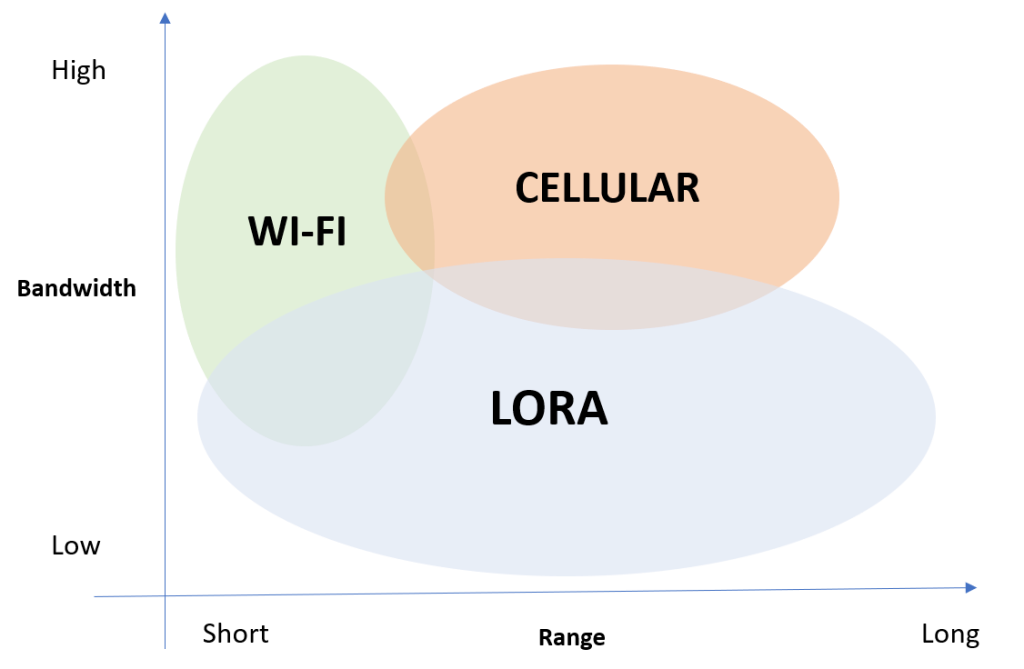
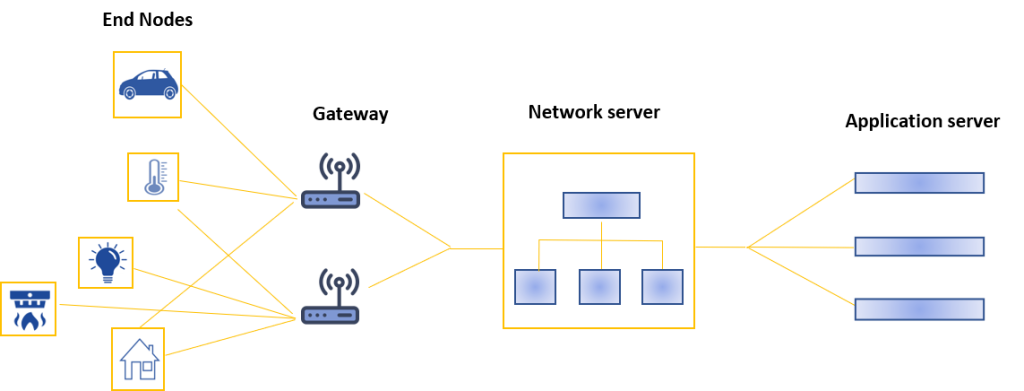
An IoT infrastructure for the active and continuous monitoring of the trolley collection areas at Fiumicino International Airport.

G-SMART is the GSE tracking system that combines different technologies (RFID, Bluetooth, ADS-B, GPS) to create the best performing solution depending on the application scenario.
IPS – indoor positioning systems – are systems that allow objects to be detected inside buildings where satellite navigation does not work very well/is not necessary; they work with both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) standards, as well as passive RFID technologies.
These systems are based on beacon or tag installed directly on the assets to be tracked; specific readers receive signals from these devices and send them to the server which processes the data obtained and makes it immediately available to the user, including information on the position of the object.
For the ADR project the system will use RFID technology for the identification and counting of baggage trolleys at the storage stations (bays) in Terminals T1 and T3 of Fiumicino International Airport, with the aim of reducing operational inefficiencies and to avoid inconveniences to the passenger relating to the search for a trolley to transport luggage.
RFID technology allows to monitor a large number of assets simultaneously and create a simple but efficient system with a reduced need for maintenance.
For the Rome Fiumicino airport we will create an IoT infrastructure made up of more than 5000 RFID tags applied directly to the trolleys (adequately mounted to avoid signal interference due to ferrous material), and an appropriate number of readers and antennas.
The data is shown in real time on a georeferenced map while a special Warning system sends alerts to operators if the number of trolleys in the bay reaches the minimum thresholds set; for each alert, a short video will be recorded from the streaming of the cameras which will then be associated with the warning notification.
The web-based software will also allow you to view and export the history of trolley movements between areas (this indicator generates the right KPIs to analyze and improve benchmarking between storage areas) and to export statistics, graphs and reports to daily management and planning support.
Finally, an improvement function is envisaged with a proactive estimate of the number of trolleys needed in the bay based on the flow of arriving passengers and baggage by connecting the tracking system to the ADR management systems.
With more than 44.4 million passengers in 2023, ADR knows how much a trolley tracking system can positively impact operational management and the Passenger Experience; in fact, a fluid trolley supply process reduces the risk of inefficiencies and delays for the passenger to a minimum, contributing to the achievement of those high performances which are worth the title of BEST AIRPORT IN EUROPE for 7 times.